Understanding Technical SEO:
 Technical SEO refers to the optimization of a website’s infrastructure and backend elements to improve its search engine visibility and overall performance. Unlike on-page and off-page SEO, which focus on content and external factors, technical SEO involves optimizing the website’s technical aspects to ensure search engines can crawl, index, and understand the content efficiently.
Technical SEO refers to the optimization of a website’s infrastructure and backend elements to improve its search engine visibility and overall performance. Unlike on-page and off-page SEO, which focus on content and external factors, technical SEO involves optimizing the website’s technical aspects to ensure search engines can crawl, index, and understand the content efficiently.
Why Is Technical SEO Important?
 Technical SEO is critically important for several reasons, as it forms the foundation upon which other aspects of search engine optimization (SEO) build. Here are key reasons why technical SEO is crucial for the success of a website:
Technical SEO is critically important for several reasons, as it forms the foundation upon which other aspects of search engine optimization (SEO) build. Here are key reasons why technical SEO is crucial for the success of a website:
Crawlability and Indexation:
Search engines use crawlers to navigate and index the vast amount of content available on the internet. Technical SEO ensures that a website is structured in a way that makes it easy for search engine bots to crawl and index its pages. This, in turn, helps the search engines understand the content and rank it appropriately in search results.Search Engine Rankings:
The technical aspects of a website directly influence its search engine rankings. Factors such as page load speed, mobile-friendliness, and secure connections (HTTPS) are considered ranking signals by search engines. Websites that perform well in these technical areas are more likely to rank higher in search results, increasing their visibility to potential users.User Experience:
Many technical SEO elements contribute to a positive user experience. For example, fast-loading pages and mobile optimization enhance the usability of a website. A site that is easy to navigate, loads quickly, and is compatible with various devices is more likely to retain users and encourage them to explore further.Mobile-First Indexing:
With the increasing use of mobile devices, search engines, particularly Google, have adopted a mobile-first approach to indexing. This means that the mobile version of a website is given priority in indexing and ranking. Technical SEO ensures that a website is responsive and optimized for mobile devices, influencing its performance in mobile search results.Duplicate Content Avoidance:
Duplicate content can confuse search engines and dilute the authority of a website. Technical SEO addresses this issue through canonicalization, using canonical tags to specify the preferred version of a page. This helps search engines understand which URL to index and rank, avoiding the negative impact of duplicate content.Website Security:
Search engines prioritize the security of user data. Websites with secure connections (HTTPS) are preferred in search rankings. Technical SEO involves implementing SSL certificates to ensure a secure browsing experience. This not only benefits search rankings but also enhances user trust and data security.Structured Data and Rich Snippets:
Implementing structured data through schema markup provides additional context to search engines about the content on a webpage. This can result in rich snippets in search results, improving the visibility and click-through rates of the pages. Technical SEO experts leverage structured data to enhance a website’s presentation in search results.Technical Issue Resolution:
Regular technical audits help identify and resolve issues that might impact a website’s performance. Technical SEO involves fixing broken links, addressing 404 errors, managing redirects, and ensuring that the website functions smoothly. This proactive approach contributes to a positive user experience and helps maintain search engine rankings.What Is The Difference Between SEO and Technical SEO?
 SEO (Search Engine Optimization) and Technical SEO are related concepts, but they refer to different aspects of the broader optimization process for websites. Let’s explore the key differences between SEO and Technical SEO:
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) and Technical SEO are related concepts, but they refer to different aspects of the broader optimization process for websites. Let’s explore the key differences between SEO and Technical SEO:
SEO (Search Engine Optimization):
Focus: SEO, in a general sense, encompasses a wide range of strategies and practices aimed at improving a website’s visibility in search engine results. It includes both on-page and off-page optimization.Components:
- On-Page SEO: Involves optimizing individual pages on a website for specific keywords. This includes optimizing content, meta tags, headers, and other elements to make them more relevant to search queries.
- Off-Page SEO: Involves external factors like link building, social media signals, and other methods to build the website’s authority and reputation.
Technical SEO:
Focus: Technical SEO specifically deals with the technical aspects of a website’s structure and performance that impact search engine rankings. It focuses on optimizing elements that affect how search engines crawl, index, and understand the content of a website. Components:- Website Speed: Ensuring fast page load times for a positive user experience and improved search rankings.
- Crawlability: Making sure search engine bots can easily navigate and index the website.
- Mobile Optimization: Optimizing the site for mobile devices and ensuring compatibility with various screen sizes.
- Security (HTTPS): Implementing secure connections through HTTPS to enhance user trust and improve search rankings.
- Structured Data Markup: Using schema markup to provide additional information to search engines about the content on a webpage.
Relationship:
While Technical SEO is a subset of the broader SEO umbrella, the two are interconnected. A technically sound website is crucial for the success of overall SEO efforts. Technical SEO lays the groundwork for on-page and off-page optimization to have a more significant impact.Timing:
SEO is an ongoing process that involves both short-term and long-term strategies to improve and maintain search rankings. Technical SEO, on the other hand, often involves initial setup and periodic maintenance but is crucial for the sustained performance of a website over time. In summary, SEO encompasses a wide range of strategies to improve a website’s overall visibility, while Technical SEO specifically addresses the technical aspects that influence search engine rankings. Both are essential for a comprehensive optimization strategy, with Technical SEO providing the structural foundation for successful SEO efforts.What is Crawling and Indexing?
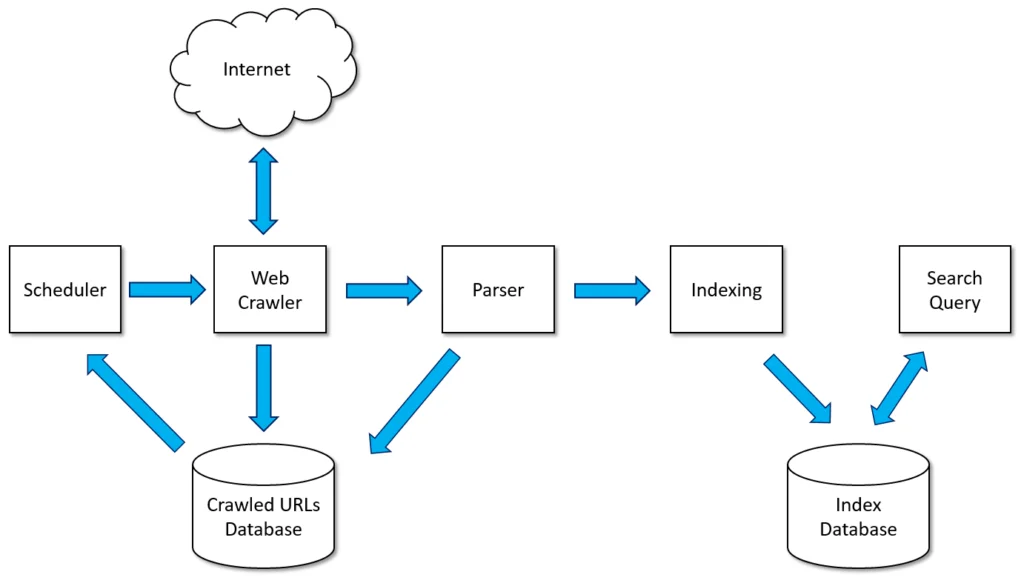 Crawling and indexing are fundamental processes that search engines use to gather and organize information from the web. These processes are crucial components of the broader field of search engine optimization (SEO). Let’s explore what crawling and indexing entail:
Crawling and indexing are fundamental processes that search engines use to gather and organize information from the web. These processes are crucial components of the broader field of search engine optimization (SEO). Let’s explore what crawling and indexing entail:
Crawling:
Crawling is the process by which search engines discover and collect information from web pages. Search engines use automated programs, commonly referred to as “crawlers,” “spiders,” or “bots,” to systematically navigate through the internet and visit websites. The primary goal of crawling is to find and retrieve content from web pages.Key Points:
Initiation: Crawling begins with a list of web addresses, known as the crawl frontier. This list may include new sites, updated pages, or previously undiscovered content. Exploration: Crawlers follow links from one page to another, creating a network of interconnected web pages. They explore both internal links (within a website) and external links (to other websites). Frequency: Popular and frequently updated sites are crawled more often to ensure that search engines have the latest information.Why Crawling is Important:
Crawling allows search engines to discover new content and updates on existing pages. It helps search engines understand the structure and content of websites.Indexing:
Indexing is the process of organizing and storing the information collected during crawling in a structured manner. The indexed data is then made available to be retrieved in response to user queries.Key Points:
Data Organization: The information collected during crawling is processed, and key elements such as keywords, meta tags, and content are extracted and stored in a database known as the index. Ranking: The index is used by the search engine’s algorithms to determine the relevance of web pages to specific search queries. Pages are ranked based on various factors like content quality, relevance, and user experience.Why Indexing is Important:
Indexing makes it possible for search engines to quickly retrieve relevant information when a user enters a search query. It forms the basis for ranking web pages in search engine results pages (SERPs).Technical SEO Best Practices
Technical SEO is a crucial aspect of optimizing a website for search engines. Here are some technical SEO best practices that can help improve your website’s performance in search engine rankings:Mobile Optimization:
Ensure your website is mobile-friendly and responsive. Google gives preference to mobile-friendly websites in its search results.Example (CSS):
/* Example of responsive design */
@media only screen and (max-width: 600px) {
body {
font-size: 14px;
}
}
Website Speed:
Page speed is a critical factor. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to analyze and improve your site’s loading times. Optimize images and use browser caching to reduce load times.Example (JavaScript):
// Example of lazy loading images
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function() {
var lazyloadImages = document.querySelectorAll("img.lazy");
lazyloadImages.forEach(function(img) {
img.src = img.dataset.src;
img.classList.remove("lazy");
});
});
SSL Encryption:
Secure your website with HTTPS. Google considers HTTPS a ranking factor, and it helps build trust with users.Example (JavaScript):
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.0.0/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<title>My Secure Website</title>
</head>
XML Sitemap:
Create and submit an XML sitemap to search engines. This helps search engines understand the structure of your site and index it more effectively.Example (XML):
<!-- Example of an XML sitemap -->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<url>
<loc>https://www.example.com/page1</loc>
<lastmod>2023-01-01</lastmod>
<changefreq>monthly</changefreq>
<priority>0.8</priority>
</url>
<!-- Additional URLs -->
</urlset>
Robots.txt:
Use a robots.txt file to control which pages search engines can or cannot crawl. Ensure important pages are accessible to search engines.Example (robots.txt):
# Example of a robots.txt file User-agent: * Disallow: /private/
Canonical URLs:
Implement canonical tags to avoid duplicate content issues. Canonical tags help search engines understand the preferred version of a page.Example (robots.txt):
<!-- Example of a canonical tag -->
<head>
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.example.com/preferred-page">
</head>
Structured Data Markup (Schema.org):
Implement structured data markup to provide search engines with more information about your content. This can enhance the display of your search results (rich snippets).Example (JSON-LD):
<!-- Example of structured data for a product -->
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "http://schema.org",
"@type": "Product",
"name": "Example Product",
"image": "http://www.example.com/product-image.jpg",
"description": "Description of the product.",
"offers": {
"@type": "Offer",
"priceCurrency": "USD",
"price": "100.00"
}
}
</script>
Header Tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.):
Use header tags to structure your content. This helps search engines understand the hierarchy and importance of different sections on a page.Example (HTML):
<!-- Example of proper heading tag usage --> <h1>Main Heading</h1> <h2>Subheading</h2> <p>Content goes here.</p>
404 Error Page:
Customize your 404 error page to guide users when they encounter a broken link or page.Example (JavaScript):
// Example of checking for broken links
var allLinks = document.getElementsByTagName('a');
for (var i = 0; i < allLinks.length; i++) {
if (allLinks[i].href.indexOf('#') === -1) {
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('HEAD', allLinks[i].href, false);
xhr.send();
if (xhr.status === 404) {
console.log('Broken link found:', allLinks[i].href);
// Implement your fix or reporting mechanism
}
}
}
URL Structure:
Use URLs that are easy to read, understand, and convey the content of the page. This includes avoiding unnecessary parameters and characters, and using keywords that reflect the page’s content.Example:
Suppose you have an e-commerce website selling shoes, and you want to create a URL for a product page: Clean and Descriptive URL:https://www.example.com/shoes/nike-air-max-2023This URL is clear, descriptive, and includes relevant keywords (brand and product name). Less Descriptive URL with Parameters:
https://www.example.com/product?id=12345&category=shoes&brand=nike&model=air-max-2023This URL is dynamic and includes parameters. It is less readable and does not provide as much information about the content.
Monitor and Audit Regularly:
Regularly audit your website for technical SEO issues. Monitor crawl errors, broken links, and other issues using tools like Google Search Console, Google PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, or GTmetrix to regularly monitor and optimize your website’s performance.Example (Google PageSpeed Insights):
Visit Google PageSpeed Insights and enter your website URL for performance recommendations.Optimize Title Tags and Meta Descriptions:
Write compelling and relevant title tags and meta descriptions for each page. These elements are crucial for click-through rates from search engine results pages (SERPs).Internal Linking:
Create a logical internal linking structure. Link relevant pages to each other using descriptive anchor text.User Experience (UX):
Improve overall user experience, as Google takes user engagement into account. This includes factors such as a clear navigation structure and easy-to-use design.Local SEO:
If applicable, optimize your website for local search by including your business name, address, and phone number on relevant pages. Utilize local schema markup.Site Security:
Regularly update your website software, plugins, and themes to ensure security. Address any security vulnerabilities promptly. By implementing these technical SEO best practices, you can enhance your website’s visibility and performance in search engine results. Keep in mind that SEO is an ongoing process, and staying informed about industry updates and algorithm changes is crucial for long-term success.What are Technical SEO Tactics?
Technical SEO Tactics are strategies focused on optimizing your website’s infrastructure, speed, indexing, and crawlability to improve search engine rankings.
Why are Technical SEO Tactics important?
They ensure search engines can efficiently crawl and index your site, improve user experience, and ultimately boost organic traffic.
Can beginners use Technical SEO Tactics?
Yes! Many tactics are beginner-friendly, though advanced strategies may require technical knowledge or tools.
How long does it take to see results from Technical SEO Tactics?
Results vary depending on your website and strategy, but improvements can often be seen within a few weeks to months.
Are there free tools to implement Technical SEO Tactics?
Yes, tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog (limited version), and PageSpeed Insights help implement many tactics for free.
Conclusion
As our exploration behind the scenes concludes, we’ve embarked on a journey through the intricate realm of Technical SEO, revealing the potent strategies that often go unnoticed but play a pivotal role in shaping online success. Just as a well-orchestrated performance seamlessly combines various elements to captivate an audience, Technical SEO weaves together the threads of site architecture, speed optimization, and indexability to create a harmonious digital symphony. The insights shared in this article serve as a roadmap for those seeking to elevate their online presence. Remember, the true power of Technical SEO lies in its ability to enhance user experience, improve site performance, and ultimately secure a prominent place in the digital spotlight.Take Action with Technical SEO Tactics
Supercharge your website performance with our SEO-optimized WordPress themes — crafted for fast loading, clean coding, and seamless technical SEO integration.


