1. Use HTTPS for a Strong Website Security Checklist

Securing your website with HTTPS ensures that all data transferred between the server and users is encrypted. This not only protects sensitive information like login credentials and payment details but also improves SEO rankings and builds trust with visitors. Beyond technical protection, HTTPS builds trust with users, as browsers now label non-HTTPS websites as “Not Secure,” which can quickly scare away visitors.
- HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts data transmitted between the user’s browser and your server using SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) protocols.
- Encryption ensures that sensitive information, such as login credentials, payment details, and personal data, remains confidential and cannot be intercepted or tampered with by malicious actors.
- Implementing HTTPS also helps build trust with users by displaying a padlock icon in the browser’s address bar, indicating a secure connection.
- Search engines like Google prioritize HTTPS websites in search results, which can improve your website’s visibility and SEO (Search Engine Optimization) ranking.
2. Keep Software Updated in Your Website Security Checklist
Regularly updating your CMS, plugins, and server software is critical to fixing vulnerabilities that hackers often exploit. Outdated systems are a common entry point for cyberattacks, making updates a must-have in your website security checklist. Automating updates where possible or scheduling regular maintenance checks ensures you stay protected without gaps.
- Regularly updating your website’s software, including the CMS (Content Management System), plugins, themes, and underlying server software, is crucial for maintaining security.
- Software updates often include patches for security vulnerabilities discovered by developers or security researchers.
- Hackers frequently exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software to compromise websites and steal sensitive data or inject malicious code.
- Stay informed about security updates released by software vendors or open-source communities and apply them promptly to minimize the risk of exploitation.
3. Strong Passwords as Part of Your Website Security Checklist

Weak passwords are one of the easiest ways attackers gain access. Enforcing strong passwords with a mix of characters, numbers, and symbols greatly reduces the chances of unauthorized access. Enforcing strong password policies that include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special symbols significantly reduces risks. For added protection, encourage users and staff to use password managers that generate and store complex passwords securely.
- Enforcing strong password policies helps prevent unauthorized access to user accounts and administrative areas of your website.
- Strong passwords are typically long, complex, and include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Discourage the use of easily guessable passwords, such as “password123” or common dictionary words.
- Encourage users to use password managers to generate and store strong, unique passwords securely.
- Consider implementing password expiration policies and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to further enhance security.
4. Implement Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) in Your Website Security Checklist
Adding 2FA creates an additional security layer by requiring users to verify their identity with a second method, such as a mobile code or biometric authentication. This makes it much harder for attackers to breach accounts. By requiring an additional layer of verification such as a mobile code, fingerprint, or authentication app, 2FA ensures that even if credentials are compromised, attackers cannot easily gain access.
- Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users and administrators to provide a second form of verification in addition to their passwords.
- Common 2FA methods include one-time codes sent via SMS, generated by authenticator apps (such as Google Authenticator or Authy), or obtained through hardware tokens.
- Even if passwords are compromised through methods like phishing or brute-force attacks, 2FA helps prevent unauthorized access by requiring a second factor that only the legitimate user possesses.
- Implementing 2FA for administrative accounts, especially those with elevated privileges, significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
5. Firewall Protection in Your Website Security Checklist
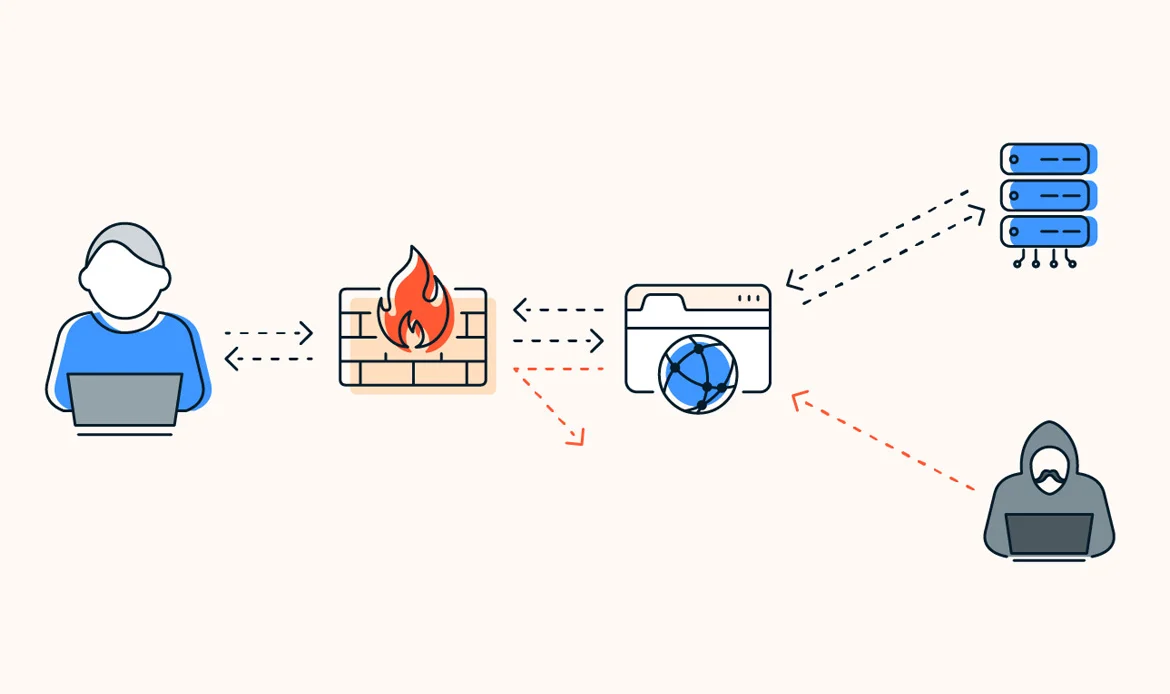
Web application firewalls (WAFs) act as the first line of defense, filtering out malicious traffic before it reaches your server. They help block threats such as SQL injections, XSS, and brute-force attacks. Whether using a hardware-based firewall or a cloud-based solution, this layer of defense plays a vital role in safeguarding against both automated bots and targeted hacks.
- A web application firewall (WAF) acts as a barrier between your website server and incoming traffic, filtering and monitoring HTTP requests and responses.
- WAFs analyze traffic patterns and block malicious requests, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and directory traversal attacks.
- They can also protect against common web-based vulnerabilities by inspecting incoming data and enforcing security policies.
- WAFs can be implemented as software or hardware appliances, or as cloud-based services, providing flexibility in deployment options.
- Regularly update WAF rules and configurations to adapt to evolving threats and ensure effective protection against emerging attack vectors.
6. Regular Backups for a Reliable Website Security Checklist
Performing regular backups ensures that even in the event of a cyberattack, hardware failure, or accidental deletion, your data can be quickly restored without major downtime or losses. Storing backups both on-site and off-site (such as in cloud storage) is recommended, and automating this process ensures you never forget. Quick recovery reduces downtime, preserves reputation, and saves valuable data.
- Regularly backing up your website’s data and files is essential for disaster recovery and ensuring business continuity.
- Backups should include not only website content but also databases, configuration files, and any custom code or scripts.
- Store backups securely offsite, preferably in a different geographic location or on a separate infrastructure, to prevent data loss in case of server failures, natural disasters, or cyberattacks.
- Automate backup processes to ensure consistency and reliability, and periodically test backup restoration procedures to verify their effectiveness.
- Consider implementing incremental backups to reduce storage space and backup duration by only backing up changes made since the last full backup.
7. Access Control

Restricting access based on user roles ensures that sensitive areas of your website are only available to authorized personnel. This minimizes the risk of accidental or malicious changes. To protect your site, limit file types, enforce size restrictions, and scan uploads for malware before accepting them. Store uploaded files outside the webroot when possible, preventing them from being directly executed on your server.
- Limiting access to sensitive directories and files on your server helps prevent unauthorized access and minimize the risk of data breaches.
- Implement least privilege access controls, granting users or processes only the permissions necessary to perform their intended tasks.
- Regularly review and audit user accounts, permissions, and access logs to identify and revoke unnecessary privileges.
- Use strong authentication mechanisms, such as SSH keys or certificate-based authentication, to secure remote access to server resources.
- Consider implementing role-based access control (RBAC) to manage permissions based on users’ roles and responsibilities within your organization.
8. File Upload Security
Unsecured file uploads can expose your site to malware. Always validate, sanitize, and restrict file types before allowing uploads, ensuring malicious scripts don’t compromise your system. This can result in stolen data, deleted records, or complete database takeover. Preventing SQL injections requires the use of prepared statements and parameterized queries, ensuring that user input is properly validated and sanitized before interacting with your database.
- File upload functionality can introduce security vulnerabilities if not implemented properly, potentially allowing attackers to upload and execute malicious files on your server.
- Validate and sanitize file uploads to ensure that only authorized file types and sizes are accepted.
- Scan uploaded files for malware and malicious content using antivirus software or third-party scanning services.
- Store uploaded files in a secure location outside the web root directory to prevent direct access and execution.
- Implement file integrity checks to verify that uploaded files have not been tampered with or modified after upload.
9. SQL Injection Prevention

SQL injections can expose or manipulate your database. Using prepared statements and parameterized queries ensures attackers cannot inject malicious code into your database queries. Preventing SQL injections requires the use of prepared statements and parameterized queries, ensuring that user input is properly validated and sanitized before interacting with your database.
- SQL injection attacks occur when attackers exploit vulnerabilities in web applications to execute malicious SQL queries against your database.
- Use parameterized queries and prepared statements to sanitize user input and prevent SQL injection vulnerabilities.
- Avoid dynamically constructing SQL queries using user-supplied data without proper validation and escaping.
- Regularly audit and validate input data to detect and mitigate potential SQL injection vulnerabilities in your web application code.
- Consider using ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) libraries or frameworks that handle parameterization and input validation automatically to reduce the risk of SQL injection.
10. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Prevention
XSS attacks inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by others. By validating input, sanitizing data, and using output encoding, you can protect users from these dangerous exploits. Protecting against XSS involves validating and sanitizing input, escaping user-generated content, and implementing security headers like Content Security Policy (CSP) to block unauthorized scripts.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users, potentially leading to theft of sensitive information or hijacking of user sessions.
- Sanitize user input and escape output to prevent attackers from injecting and executing scripts in your web pages.
- Use security headers, such as Content Security Policy (CSP), to restrict the sources from which scripts can be loaded and executed.
- Implement input validation and output encoding to filter and neutralize malicious XSS payloads, preventing them from being executed in users’ browsers.
- Regularly audit and review your web application code for XSS vulnerabilities, and leverage automated security testing tools to identify potential attack vectors.
11. Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) Protection

CSRF tricks users into performing actions they didn’t intend, like changing passwords or making payments. Using unique tokens for requests ensures that only genuine interactions are processed. Implementing anti-CSRF tokens ensures that each request is legitimate and originates from the correct user session. This small but powerful measure prevents attackers from exploiting authenticated user sessions.
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) attacks trick authenticated users into unknowingly performing actions on a website without their consent.
- Use CSRF tokens to validate and verify that the actions performed on your website originate from legitimate sources.
- Generate unique CSRF tokens for each user session or form submission and include them in requests to verify their authenticity.
- Validate CSRF tokens on the server-side to ensure that requests are coming from authorized users and not from malicious attackers.
- Implement measures such as SameSite cookies and anti-CSRF tokens to mitigate the risk of CSRF attacks and protect users’ sensitive actions.
12. Content Security Policy (CSP)
Implementing a Content Security Policy (CSP) helps prevent unauthorized scripts and malicious code injections by controlling which resources your website can load. As part of a Website Security Checklist, CSP strengthens protection against XSS, improves user trust, and ensures compliance with modern security standards.
✔. Preventing XSS Attacks in Your Website Security Checklist
One of the primary purposes of a Content Security Policy is to defend against Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks. By restricting which scripts can run on a website, CSP blocks unauthorized JavaScript injections that could steal user data, redirect traffic, or execute harmful code. This adds a powerful layer of protection that works alongside traditional input validation and sanitization.
✔. Defining Trusted Content Sources for a Strong Website Security Checklist
CSP allows you to specify trusted domains for resources like scripts, images, stylesheets, and media. For example, you can configure your website to load content only from your own domain and verified third-party providers. This reduces the risk of loading malicious files from unknown or compromised sources, thereby improving the integrity of your website.
✔. Enhancing User Trust and Compliance with a Website Security Checklist
Beyond technical protection, implementing a CSP also builds user confidence. When visitors know that a site takes proactive measures to secure their data, it improves credibility and engagement. Additionally, adopting CSP helps organizations comply with modern data protection standards and industry best practices, making it a vital part of any website security checklist.
13. Secure File Permissions
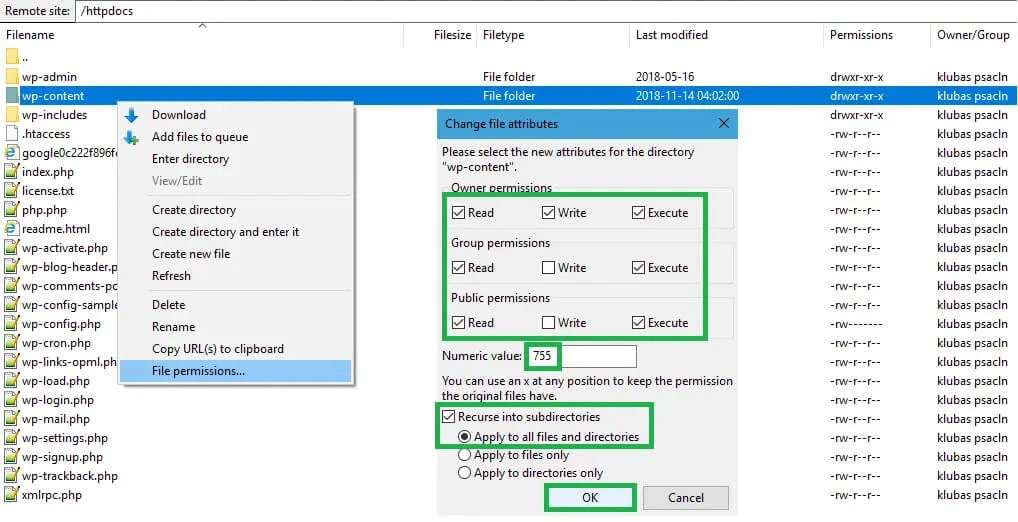
Improper file permissions can expose your website to attacks. Restrict permissions so that files and directories are only accessible by necessary users, reducing the risk of exploitation. For instance, configuration files containing sensitive credentials should be read-only for the server and inaccessible to the public.
- Setting appropriate file permissions on your server helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive files and directories.
- Use the principle of least privilege to grant permissions only to the users or processes that require them to perform specific tasks.
- Set directory permissions to prevent unauthorized listing of directory contents and restrict file permissions to limit access to sensitive data.
- Regularly audit and review file permissions to identify misconfigurations or overly permissive settings that could expose your website to security risks.
- Consider using access control lists (ACLs) or file integrity monitoring tools to enforce and monitor file permissions more effectively.
14. Monitoring and Logging
Constant monitoring and logging help detect unusual activities, failed login attempts, or malware behavior. By analyzing logs, you can identify and respond to threats before they escalate. Centralized logging tools and security information systems help analyze data in real-time, enabling faster responses to potential breaches.
- Monitoring your website’s traffic and server logs helps detect and respond to security incidents and suspicious activities in real-time.
- Implement logging mechanisms to record important events, such as login attempts, access to sensitive resources, and system errors.
- Use intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to analyze network traffic and identify potential security threats.
- Set up alerts and notifications to notify administrators of suspicious activities or anomalies detected in server logs and network traffic.
- Regularly review and analyze log data to identify patterns, trends, and potential security incidents, and take appropriate action to mitigate risks.
15. Regular Security Audits

Conducting regular security audits helps uncover vulnerabilities before hackers do. These audits include penetration testing, code reviews, and vulnerability assessments to ensure strong defense. Regular audits ensure that your website security checklist stays current and effective against evolving cyber risks.
- Conducting regular security audits and vulnerability assessments helps identify and address potential security weaknesses in your website and infrastructure.
- Perform code reviews, penetration testing, and security scans to identify vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and insecure practices.
- Use automated security testing tools and manual testing techniques to identify common security issues, such as SQL injection, XSS, CSRF, and insecure authentication mechanisms.
- Prioritize and remediate identified vulnerabilities based on their severity and potential impact on your website’s security.
- Develop and follow a formal security audit process that includes scheduling regular audits, documenting findings, and tracking remediation efforts.
16. Incident Response Plan
Having a clear incident response plan allows your team to react quickly in the event of a breach. This reduces downtime, limits damage, and ensures a structured recovery process. A structured response outlines the steps to take in the event of a breach, including isolating affected systems, notifying stakeholders, restoring backups, and reporting incidents if required by law. This preparation minimizes damage and speeds up recovery.
- Developing an incident response plan is essential for effectively responding to security incidents and minimizing their impact on your website and organization.
- Define roles and responsibilities for incident response team members, including communication channels, escalation procedures, and decision-making authority.
- Establish predefined steps and procedures for detecting, containing, investigating, and remedying security incidents, such as data breaches, malware infections, or denial-of-service attacks.
- Document incident response procedures in detail and ensure that all relevant stakeholders are familiar with their roles and responsibilities.
- Conduct regular drills and exercises to test the effectiveness of your incident response plan and identify areas for improvement.
17. Educate Users
End-users are often the weakest security link. Providing training on phishing, password hygiene, and safe browsing practices significantly reduces human-related security risks. Clear security awareness programs empower users to recognize and avoid threats before they cause harm.
- Educating users about cybersecurity best practices is crucial for raising awareness and reducing the risk of security incidents caused by human error.
- Provide training and awareness programs to help users recognize common threats, such as phishing emails, social engineering attacks, and malicious websites.
- Teach users how to create strong, unique passwords, and encourage them to use password managers to securely store and manage their credentials.
- Emphasize the importance of keeping software and devices up to date with the latest security patches and updates to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Foster a culture of security awareness within your organization by promoting open communication, encouraging reporting of security incidents, and rewarding proactive security behavior.
18. Third-Party Integrations
Plugins, APIs, and third-party tools can introduce vulnerabilities. Always vet providers, limit unnecessary integrations, and keep them updated to maintain security. Vetting third-party providers, removing unnecessary integrations, and keeping them updated are essential for reducing risks. Choosing only reputable vendors with a proven security track record is an important part of long-term protection.
- Vetting third-party plugins, libraries, and services for security vulnerabilities is essential to ensure that they do not introduce new risks to your website.
- Research the reputation and security track record of third-party vendors before integrating their products or services into your website.
- Regularly review and monitor third-party integrations for security updates, patches, and vulnerabilities disclosed by vendors or security researchers.
- Limit the number of third-party integrations to reduce the attack surface and potential security risks associated with external dependencies.
- Consider using security tools and services that provide visibility and monitoring of third-party integrations to detect and mitigate security threats.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks can disrupt your website’s availability and cause downtime by overwhelming your server with a flood of malicious traffic.
- Implement DDoS protection mechanisms, such as rate limiting, traffic filtering, and cloud-based DDoS mitigation services, to mitigate the risk of DDoS attacks.
- Use network and application-layer DDoS protection solutions to detect and block malicious traffic before it reaches your website’s infrastructure.
- Monitor network traffic and server performance metrics to identify signs of a DDoS attack and respond quickly to minimize its impact.
- Develop a DDoS response plan that outlines steps for mitigating DDoS attacks, including communication procedures, traffic rerouting strategies, and coordination with DDoS mitigation service providers.
- Providing regular security training for your development and operations teams helps ensure that they stay up to date on the latest security threats, vulnerabilities, and best practices. Offer training sessions, workshops, and online courses covering topics such as secure coding practices, vulnerability management, and incident response procedures.
- Encourage team members to obtain relevant security certifications and participate in industry conferences, seminars, and community events to expand their knowledge and skills.
- Foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement by promoting collaboration, knowledge sharing, and feedback among team members.
- Regularly assess and evaluate the effectiveness of your security training programs and adjust them as needed to address emerging threats and evolving security requirements.
19. DDoS Protection
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks can cripple a website by overwhelming servers. Using DDoS protection services ensures your site remains accessible during large-scale traffic surges. Implementing DDoS protection solutions, such as content delivery networks (CDNs) or cloud-based mitigation tools, ensures your site remains online and functional even during large-scale attack attempts.
20. Regular Security Training
Continuous training for staff ensures they remain aware of evolving threats and the latest best practices. A well-informed team is your strongest defense against cyber risks. This continuous learning builds a culture of awareness and makes your website security checklist stronger over time.
Why is a Website Security Checklist important?
A Website Security Checklist helps identify and implement essential measures like HTTPS, firewalls, and regular updates to protect against cyber threats and data breaches.
What are the top 3 things to secure a website quickly?
Start with enabling HTTPS, using strong passwords with two-factor authentication (2FA), and regularly updating your CMS and plugins.
How often should I perform security audits?
Ideally, websites should undergo security audits at least once every quarter, but mission-critical platforms may require monthly reviews.
Can small business websites be targeted by hackers?
Yes. Hackers often target small websites assuming they lack strong defenses, making a website security checklist even more crucial for small businesses.
Does website security improve SEO rankings?
Absolutely. Google prioritizes HTTPS-enabled and secure websites, meaning stronger security can enhance your search engine visibility.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of the Website Security Checklist, it’s evident that safeguarding your online presence requires a multi-faceted approach, encompassing technical solutions, proactive management, and user education. In an era where cyber threats continue to evolve in sophistication and frequency, investing in robust security measures isn’t just a precaution—it’s a necessity for businesses, organizations, and individuals alike. By implementing the strategies outlined in this checklist, you can fortify your website against common vulnerabilities, mitigate the risk of security breaches, and uphold the trust of your visitors and customers. So, embrace the Checklist of Website Security as your roadmap to a safer, more secure online journey, and pave the way for a resilient and trustworthy digital presence in today’s interconnected world.Stay Ahead of Hackers – Secure Your Website Today
Protect your online presence with our secure WordPress themes — built with clean code, regular updates, and strong protection against vulnerabilities. Stay one step ahead of hackers!


