The Art of WordPress Theme Customization: Tips and Tricks” focuses on enhancing the appearance and functionality of your WordPress site through effective theme customization. It provides valuable insights and practical tips on modifying themes, from basic adjustments like color schemes and fonts to advanced changes such as custom layouts and functionalities.
Whether you’re new to WordPress or an experienced user, these Theme Customization Tips will help you create a website that is both visually appealing and highly functional, ensuring an optimal user experience and improved site performance. In this guide, we’ll share practical Theme Customization Tips that will help you enhance your site’s design, functionality, and performance, whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned WordPress user.
Smart Customization Hacks to Make Your WordPress Theme Stand Out
1. Adding Custom Forms

Forms allow visitors to interact with your site. Use tools like:
- Contact Form Plugins: Popular options like Contact Form 7, WPForms, or Gravity Forms let you create forms for inquiries, feedback, or lead generation.
- Custom Form Styling: Style forms with CSS to match your website’s aesthetics
// functions.php or your custom plugin file
input[type="text"], textarea {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
padding: 10px;
width: 100%;
}
2. Adding Custom Headers and Footers
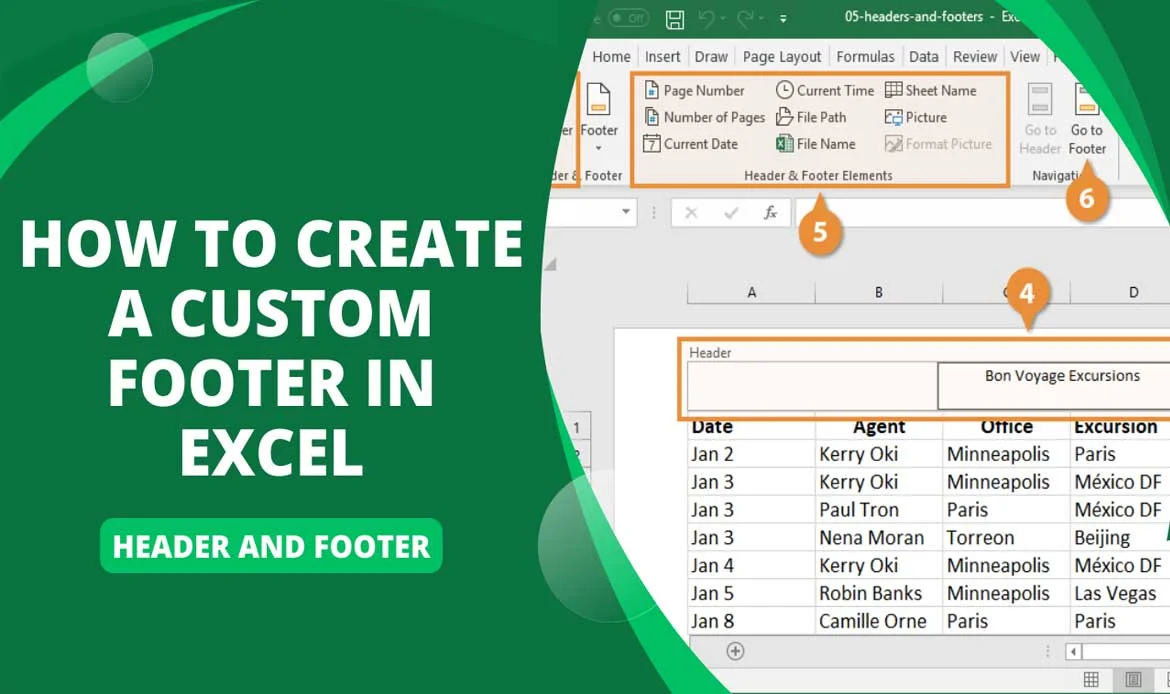
Customizing headers and footers gives your site a polished look:
- Theme Options or Builders: Many themes include header and footer editors in the Customizer or theme settings.
- Using Plugins: Tools like Elementor Pro or Header Footer Elementor let you create custom headers and footers with drag-and-drop ease. These plugins offer powerful Theme Customization Tips to simplify the process for beginners and professionals alike.
- Manually Editing Templates: Modify header.php and footer.php to add custom elements like social icons or a newsletter signup form.
3. A Guide to Using PHP Functions

To take your WordPress theme customizations further, understanding PHP functions is essential. PHP allows you to enhance your theme’s functionality beyond basic options.
- Functions.php: Use this file to add custom functions, hooks, or filters to extend your theme’s capabilities. It’s a core place to include custom code like modifying how posts are displayed or adding new features.
- Custom Functions: Create new functions to improve the performance or functionality of your site, such as customizing query loops or integrating third-party APIs.
- Best Practices: Always ensure your PHP code is clean, well-commented, and tested to prevent errors and ensure stability.
- Backup and Test: Before modifying PHP files, back up your website, and test changes on a staging site to avoid disrupting the live site.
4 Adding Custom Widgets

Widgets enhance your site by displaying dynamic content in specific areas like sidebars or footers. To add custom widgets:
1. Create a Widget Area
Add this to your theme’s functions.php:
function custom_widget_area() {
register_sidebar(array(
'name' => 'Custom Widget Area',
'id' => 'custom-widget-area',
'before_widget' => '',
));
}
add_action('widgets_init', 'custom_widget_area');
5. Adding Micro-Animations

Animations make your website feel modern and interactive. Tools to add animations:
CSS Animations:
// Inside your loop
.fade-in {
animation: fadeIn 2s ease-in-out;
}
@keyframes fadeIn {
from { opacity: 0; }
to { opacity: 1; }
}
Animation Plugins: Use Animate It! or Lottie Player to add advanced animations with minimal effort.
6. Creating Custom 404 Pages
A creative 404 page enhances user experience and encourages visitors to stay on your site.
- Custom Templates: Create a custom 404.php template in your theme folder.
- Add Useful Links: Include links to popular pages or a search bar to guide users.
.error-404 {
text-align: center;
padding: 50px;
}
.error-404 h1 {
font-size: 48px;
color: #0073aa;
}
7. Creating Custom Navigation Menus

Navigation menus are key to guiding users through your site. Customize them by: Editing Menu Locations: Many themes provide pre-set menu locations. You can register custom ones:
// Inside your loop
function custom_menu_location() {
register_nav_menus(array(
'header-menu' => __('Header Menu'),
'footer-menu' => __('Footer Menu'),
));
}
add_action('init', 'custom_menu_location');
8. Customizing with Plugins

Plugins are indispensable for adding functionality without altering core theme files. Here’s how to make the most of them:
Drag-and-Drop Page Builders:
- Elementor: Intuitive interface for building custom designs.
- Divi Builder: Powerful visual editor with built-in optimization tools.
- Gutenberg Enhancers: Extend the default block editor with plugins like Kadence Blocks.
Functional Plugins:
- Add a contact form with WPForms or Contact Form 7.
- Include SEO tools like Yoast SEO or RankMath.
- Create custom fields with Advanced Custom Fields (ACF).
9. Customizing WooCommerce Themes

If your website involves e-commerce, tailoring WooCommerce-specific themes is essential. Tips for customizing WooCommerce:
- Product Page Layouts: Modify product display settings in the theme’s options or use a page builder like Elementor Pro. These are great Theme Customization Tips to personalize the shopping experience.
- Custom Checkout Fields: Add or edit checkout fields using the WooCommerce Checkout Field Editor plugin.
- Custom Templates: Override WooCommerce templates by copying them from the plugin folder to your theme’s woocommerce directory and modifying as needed.
10. Enhancing Accessibility

Accessibility ensures your website is usable by all, including people with disabilities.
- ARIA Roles: Add ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) roles to your HTML to make elements screen-reader friendly.
- Keyboard Navigation: Ensure your site is navigable via keyboard for those who cannot use a mouse.
- Plugins for Accessibility: Use plugins like WP Accessibility to identify and fix common accessibility issues.
11. Implementing Custom Fonts
Typography plays a vital role in defining the personality of your website. Here’s how to add and customize fonts:
Google Fonts Integration:
Many themes support Google Fonts, which can be managed through the WordPress Customizer or theme settings. If not, you can manually include them:// Inside your loopAdd this to your header.php or enqueue it in functions.php. Using Custom Fonts: Upload your custom font files (e.g., .woff, .ttf) to your server and link them via CSS:
// Inside your loop
@font-face {
font-family: 'MyCustomFont';
src: url('path-to-font/MyCustomFont.woff') format('woff');
}
body {
font-family: 'MyCustomFont', sans-serif;
}
Font Plugins: Plugins like Use Any Font simplify the process of adding custom fonts without coding.
12. Learn from the Community

The WordPress community is vast and supportive. Join forums, attend meetups, or explore tutorials to stay updated with the latest trends and techniques.
- Forums and Discussion Boards: Platforms like the WordPress.org forums, Stack Overflow, and Reddit’s WordPress community are great places to ask questions, share ideas, and troubleshoot issues with fellow users.
- Online Tutorials and Courses: Many community-driven sites, like WPBeginner, offer in-depth tutorials for both beginners and advanced users, making it easy to learn new customization techniques at your own pace.
- Meetups and WordCamps: Attend local meetups or WordPress conferences to connect with seasoned developers, exchange tips, and stay ahead of the latest trends in theme customization. Events like these often share invaluable Theme Customization Tips directly from experts.
13. Leveraging the WordPress Customizer

The WordPress Customizer offers a visual interface to tweak your site’s appearance without diving into code. Advanced features include:
- Global Styles: Change typography, background colors, and button styles universally.
- Dynamic Headers and Footers: Some themes support header and footer builders directly within the Customizer.
- Site Identity: Customize your logo, site title, tagline, and favicon.
14. Mastering CSS for Advanced Customization
CSS is your go-to tool for detailed design tweaks. Here’s how to level up your CSS skills:
- Using Developer Tools: Right-click on an element and choose “Inspect” to see the associated CSS rules. This helps you identify and target specific classes or IDs.
Change button colors:
// Inside your loop
.button-class {
background-color: #ff5722;
color: #ffffff;
}
Adjust margins or padding:
// Inside your loop
.section-class {
margin: 20px;
padding: 15px;
}
CSS Best Practices: Organize your custom CSS into sections, use comments for clarity, and keep it minimal to avoid bloated code.
15. Theme Customization Tips: Modifying Template Files
For deeper customizations, you may need to edit the theme’s template files. This process requires a basic understanding of PHP and HTML.
- Functions.php: Add custom code snippets here to extend your theme’s functionality.
- Page Templates: Create or modify page templates to achieve unique layouts for specific pages.
- Backup Your Work: Always back up your files before editing templates to avoid losing work due to errors.
16. Staying Updated

Themes, plugins, and WordPress itself frequently release updates. Always:
- Backup Before Updating: Use plugins like UpdraftPlus to create a full site backup.
- Use Staging Environments: Test updates in a staging environment before applying them to your live site.
17. Testing and Debugging
Proper testing ensures that your customizations don’t disrupt functionality. Best practices include:
- Responsive Testing: Use tools like BrowserStack or Responsinator to preview your site across various devices.
- Debugging Issues: Enable debugging in wp-config.php
// Inside your loop
define('WP_DEBUG', true);
Plugins like Debug Bar can also help identify errors.
18. Understanding Theme Basics

WordPress themes serve as the visual foundation of your website, and knowing their structure is vital for customization. Key components include:
- Template Files: PHP files that dictate how specific pages are displayed. For example, index.php is the main template, while single.php handles single posts.
- Stylesheet: (style.css): Controls the overall visual styling, such as fonts, colors, and layouts.
- JavaScript Files: Adds interactive features like sliders, pop-ups, or animations.
- Theme Functions: (functions.php): Allows you to extend or modify the theme’s features using PHP snippets.
Child Themes in Detail:
Child themes are essential when customizing themes. They prevent your changes from being overwritten during theme updates. Here’s how to create one:// Inside your loop /* Theme Name: Your Child Theme Name Template: parent-theme-folder-name */3. Import the parent theme’s stylesheet:
// Inside your loop
@import url("../parent-theme-folder/style.css");
4.Add a functions.php file to enqueue the parent theme’s styles.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I personalize a WordPress theme to match my brand identity?
You can easily tailor your WordPress theme using the built-in Customizer to adjust colors, fonts, and layouts. For deeper control, use a child theme or a page builder like Elementor to visually align your site with your brand’s style and tone.
Is it possible to customize my theme without coding skills?
Yes! Many WordPress themes come with drag-and-drop builders, theme options panels, and live preview features. These tools make it simple to change designs, add widgets, and modify content layouts without writing any code.
How do I maintain performance after customizing my theme?
To keep your site fast, use lightweight themes, optimize images, and avoid unnecessary plugins. Minify CSS and JavaScript, enable caching, and test your site speed regularly using tools like GTmetrix or Google PageSpeed Insights.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering Theme Customization Tips is essential for creating a WordPress website that stands out and meets your unique needs. By exploring the tools, techniques, and best practices outlined in this guide, you can confidently enhance your site’s design, functionality, and user experience, ensuring it reflects your vision and goals.
With the right tools and techniques, you can enhance your site’s design and usability to match your vision.By applying the techniques and best practices shared, you can ensure your site stands out, aligns with your vision, and provides an excellent user experience.
Remember, every customization decision should prioritize your audience’s needs and align with your website’s goals. With these Theme Customization Tips, you can confidently create a website that not only looks great but performs exceptionally well, leaving a lasting impression on your visitors.
Unlock the Full Potential of Your WordPress Site Today!
Upgrade your design workflow today! Use Elementor and optimized themes to craft visually captivating, functional, and future-ready WordPress websites in 2025.


